Artificial Intelligence Management of Diseases
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a valuable tool in the medical field, contributing significantly to the diagnosis, treatment, and management of diseases.
While AI cannot directly “cure” diseases in the traditional sense, it can assist medical professionals and researchers in various ways that lead to more effective and efficient healthcare outcomes. Here are some of the key contributions of AI in addressing health issues:
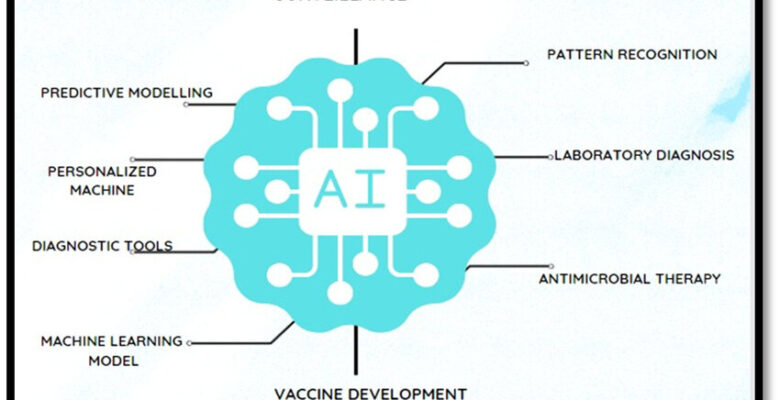
1. **Diagnostic Support**: AI algorithms, particularly those based on machine learning, can analyze large datasets of medical images, patient records, and lab results to detect patterns that are indicative of diseases. For example, AI systems are used to identify signs of cancer in imaging studies, such as mammograms, with a high degree of accuracy, often surpassing human error rates. These systems can help radiologists and pathologists make more precise diagnoses, leading to earlier and more effective treatment.
2. **Drug Discovery and Development**: AI is playing a crucial role in accelerating the drug discovery process by analyzing vast amounts of chemical and biological data to identify potential drug candidates. It can predict how new molecules will interact with disease targets and assess their safety and efficacy, thereby reducing the time and cost of bringing new drugs to market.
3. **Predictive Analytics**: AI can be used to predict the likelihood of disease progression or patient outcomes based on various factors such as genetic data, lifestyle, and environmental conditions. This helps in tailoring treatments to individual patients and making informed decisions regarding preventive care.
4. **Treatment Planning**: In fields like oncology, AI can assist in creating personalized treatment plans by analyzing a patient’s genetic profile and medical history to determine the most effective combination of therapies. This is known as precision medicine and can lead to better patient outcomes and fewer side effects.
5. **Monitoring and Management**: AI can help monitor patients with chronic diseases by analyzing real-time data from wearable devices and electronic health records. It can alert medical staff to potential health issues before they become critical, allowing for timely interventions and better management of conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and mental health disorders.
6. **Clinical Decision Support**: AI systems can provide evidence-based recommendations to healthcare providers, helping them make informed decisions by synthesizing vast amounts of medical knowledge and the latest research findings.
7. **Vaccine Development**: AI is used in the design and testing of vaccines by simulating interactions between pathogens and the human immune system. This can speed up the development process and increase the chances of creating effective vaccines against new or emerging diseases.
8. **Epidemiology and Public Health**: AI models can track and predict the spread of infectious diseases, enabling public health officials to implement timely interventions such as quarantine measures or targeted vaccination campaigns.
9. **Research and Development**: AI is instrumental in analyzing complex biomedical data to uncover new insights into disease mechanisms and potential treatment strategies. It can also assist in the identification of biomarkers for early detection and diagnosis of diseases.
10. **Clinical Trials**: AI can optimize the design and analysis of clinical trials, leading to faster and more reliable results. It can help in patient recruitment, monitoring, and data analysis, which can accelerate the development of new treatments.
While AI does not directly cure diseases, it is a powerful adjunct to human expertise that can lead to better healthcare outcomes. It is important to note that the integration of AI into medical practice is still in its early stages, and its effectiveness is contingent upon the quality of the data it is trained on, the algorithms used, and the interpretation of its results by medical professionals.
Additionally, ethical considerations, such as data privacy and the potential for algorithmic bias, must be carefully addressed to ensure equitable and responsible use of AI in healthcare.